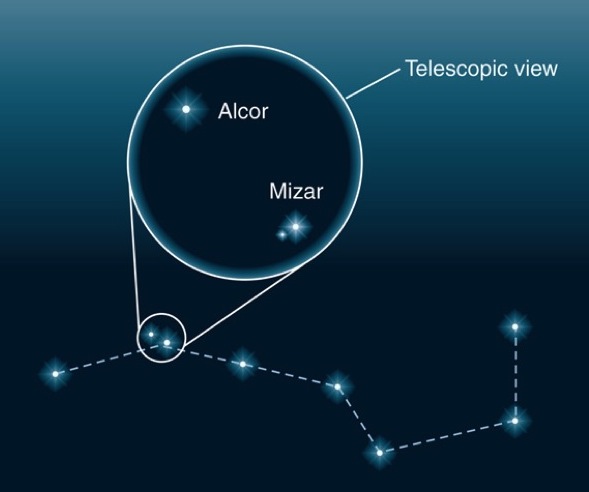
Apparent double stars (e.g. Mizar and Alcor, 12 arcmin separation)
Binary stars
Binaries are actually very common. (Mizar itself consists of two stars 14'' apart; Mizar A and Mizar B, as well as Alcor, are also found to be binaries.)
- visual binaries
- astrometric binaries
- spectrum binaries
- spectroscopic binaries
- eclipsing binaries
- For visual binaries
P2 = 4π2a3 / G(m1+m2)
m1+m2 = a3 / P2 (in M⊙, AU, yr)
* some problems: distance, inclination, mass ratio
- One example for astrometric binaries: Sirius
In 1844, the wavy path of its proper motion found
In 1862, Sirius B discovered, m=7.5; so it became a visual binary
MA~ 2.35 M⊙
MB~ 0.98 M⊙, size ~ R⊕, a white dwarf!
- From many determinations of stellar mass in binaries, mainly from
spectroscopic binaries (see below), a mass-luminosity relation was found for
main-sequence stars:
L is roughly proportional to M3.5.
- The mass function of a spectroscopic binary